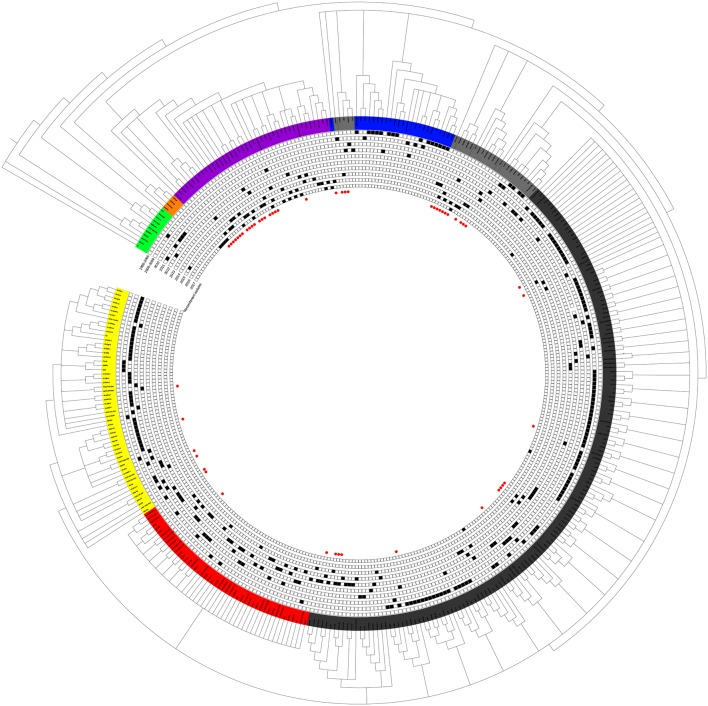
Genetic Diversity of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV) From 1996 to 2017 in China.
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) is one of essentially the most devastating illnesses of the worldwide swine trade. The causative agent porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) was first remoted in China in 1996 and has advanced rapidly over the past 20 years. To absolutely perceive virus variety, epidemic scenario in the sphere, and make […]